Summary
On July 24, 2024, CrowdStrike Intelligence identified an unattributed spearphishing attempt delivering an inauthentic CrowdStrike Crash Reporter installer via a website impersonating a German entity. The website was registered with a sub-domain registrar. Website artifacts indicate the domain was likely created on July 20, 2024, one day after an issue present in a single content update for CrowdStrike’s Falcon sensor — which impacted Windows operating systems — was identified and a fix was deployed.
After the user clicks the Download button, the website leverages JavaScript (JS) that masquerades as JQuery v3.7.1 to download and deobfuscate the installer. The installer contains CrowdStrike branding, German localization and a password required to continue installing the malware.
Details
Spearphishing Page
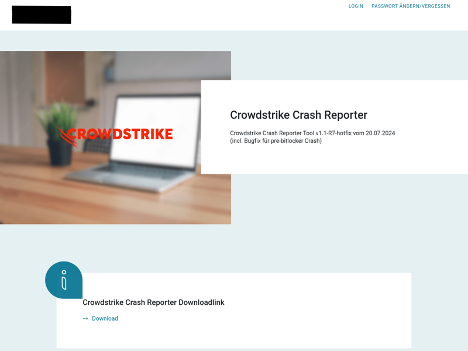
The threat actor leveraged a spearphishing page hosted on a URL with the format http[:]//{German Entity}.it[.]com/crowdstrike/. This spearphishing page presented the targeted victim with a download link to a ZIP file containing a malicious InnoSetup installer (Figure 1). The website it[.]com is a legitimate domain registrar, and the threat actor likely created the spearphishing page after the Falcon sensor update was deployed.
Because the website provider is a domain registrar, CrowdStrike Intelligence could not determine when the subdomain was created. However, the webpage’s timestamp indicates the InnoSetup1 installer was created on July 20, 2024 (hotfix vom 20.07.2024).
The spearphishing page displays the branding of the targeted company and CrowdStrike. It requests that the victim download CrowdStrike Crash Reporter, a tool not developed by CrowdStrike or distributed through official CrowdStrike communication channels (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Phishing page displaying the targeted company’s and CrowdStrike’s branding
The JS serving the malicious executable masquerades as JQuery v3.7.1 — an open-source JS library — at the HTTP endpoint /crowdstrike/media/jquery-3.7.1.min.js. The code used to serve the malicious executable is contained at the beginning of the file and appended with the benign code for JQuery v3.7.1, likely in an attempt to evade detection.
The spearphishing site calls the function gApiAsync, which is defined in jquery-3.7.1.min.js; the first parameter is a relative path to the file media/disabled.svg. After clicking the download button, the user triggers the function d(), which executes the gApiAsync function (Figure 2).
Figure 2. OnClick event triggering the download
Next, the JS makes an HTTP GET request for the file media/disabled.svg, which is then parsed using a regex that searches for any text not in double quotes after the pattern AAAAAAAAAAAAAAw. The resulting string is Base64-decoded and provided to the user to download via a JS Blob2 as a Portable Executable (PE) file. If any errors occur, the developer console displays error messages masquerading as issues with JQuery v3.7.1 (Figure 3).
Figure 3. JS used to deobfuscate delivered executable
Installer
The inauthentic installer (SHA256 hash: a7516a15e1857996373191795c79244c8f5c8deb1f17ba5dbadeac28e18ec1c7) has the filename CrowdStrike_Crash_Reporter_Setup_8.R3.exe and uses German-language prompts, likely reflecting the threat actor’s targeting profile (Figure 4).
Figure 4. InnoSetup initial installer window
After starting the installation, the victim is prompted to input a “Backend-Server”. Failure to provide the specific input results in an error message (machine translation: A connection error has occurred), preventing the installation from completing (Figures 5 and 6). However, initial analysis indicates the installer did not perform any connectivity checks.
Figure 5. URL check
Figure 6. Error message
The InnoSetup installer is password-protected and contains an InnoSetup script (install_script.iss) and two additional files (csmon8.dat and Java8Runtime.exe). As of this writing, CrowdStrike Intelligence could not recover the final payload but did recover the file metadata (Table 1).
Path
File Size
File Creation Timestamp (UTC)
{localappdata}Javacsmon8.dat
249736
2024-07-23 13:28
{localappdata}JavaJava8Runtime.exe
24216136
2024-07-23 13:02
install_script.iss
2750
2024-07-24 16:46
Table 1. Malicious InnoSetup Installer listed contents
The InnoSetup Installer executable file-creation timestamp (2024-07-12 07:26:53 UTC) aligns with the date of the sensor content update (July 19, 2024) and the creation timestamps of the installer files, likely indicating the threat actor used timestomping as an anti-forensic technique.
Assessment
CrowdStrike Intelligence assesses with high confidence that the attack is likely targeted based on the following observations:
The victim is required to enter a specific password (under the pretext of a “Backend-Server”) that is likely only known to the targeted entities
Using a German-language spearphishing website and prompts for the installer indicates the actors are only targeting German-speaking CrowdStrike customers affected by the Falcon sensor content issue
The threat actor appears to be highly aware of operations security (OPSEC) practices, as they have focused on anti-forensic techniques during this campaign. For example, the actor registered a subdomain under the it[.]com domain, preventing historical analysis of the domain-registration details. Additionally, encrypting the installer contents and preventing further activity from occurring without a password precludes further analysis and attribution.
Recommendations
These recommendations can be implemented to help protect against the activity described in this report.
Only accept updates delivered through official CrowdStrike channels, and adhere to CrowdStrike support teams’ technical guidance
Check website certificates on the download page to ensure downloaded software originates from a legitimate source
Train users to avoid executing files from untrusted sources
Enable download protection that can issue warnings about potentially harmful websites or downloads
Appendix
Falcon LogScale Queries
These Falcon LogScale queries detect the activity described in this report.
The following Falcon LogScale query hunts for suspicious filenames associated with the inauthentic CrowdStrike installer identified in this alert:
event_platform=Win | in(field=FileName, values=[“Crowdstrike_crash_reporter_v1.1-R7.zip”, “CrowdStrike_Crash_Reporter_Setup_8.R3.exe”, “CrowdStrike_Crash_Reporter_Setup_8.R3.tmp”])
The following Falcon LogScale query hunts for HTTP GET requests to /media/disabled.svg that contain the obfuscated payload:
event_platform=Win
| #event_simpleName=*HttpRequest*
| concat([HttpRequestHeader, HttpsRequestHeader], as=”combined”)
| combined = /^GET /media/disabled.svg / HTTP/
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
This table details the IOCs related to the information provided in this report.
Description
Detail
Timestamp (UTC)
ZIP lure (Crowdstrike_crash_reporter_v1.1-R7.zip)
41143b2e4bbb9279ba0bbb375748530cc4887cc965967e5c0cc9a39dc44937d6
2024-07-23 13:41:54 (modified)
Malicious InnoSetup installer executable (CrowdStrike_Crash_Reporter_Setup_8.R3.exe)
a7516a15e1857996373191795c79244c8f5c8deb1f17ba5dbadeac28e18ec1c7
2024-07-12 07:26:53 (compiler timestamp; likely timestomped)
Delphi executable (CrowdStrike_Crash_Reporter_Setup_8.R3.tmp)
80304da1e333ed581378797ad8b0b8d81a8ac5928b83423702f0de30f1616225
2024-07-12 07:26:52 (compiler timestamp; likely timestomped)
Spearphishing URL
http[:]//{German Entity}.it[.]com/crowdstrike/
n/a
Obfuscated version of Crowdstrike_crash_reporter_v1.1-R7.zip
http[:]//{German Entity}.it.com/crowdstrike/media/disabled.svg
n/a
Spearphishing domain IPv4
4.180.4[.]19
n/a
JS downloader
99bb0f05fd135218a5c4b8cac42e58274086b543d001d7227c8f6a2b7722f425
n/a
Likely next-stage executable Java8Runtime.exe
82ef869e8f7accde731f8c289f19436347a30af1d53c8f61bde5bac8bc91ad1a
unknown
Table 2. IOCs
MITRE ATT&CK
This table details the tactics and techniques described in this report.
Tactic
Technique
Observable
Initial Access
T1566.001 – Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment
The spearphishing page heavily targeted a German entity and delivered an inauthentic CrowdStrike crash-reporting application
T1566.002 – Phishing: Spearphishing Link
The spearphishing link was likely sent to the German entity over email
Execution
T1204.002 – User Execution: Malicious File
The user is required to enter a password to decrypt the installer contents for the next stages
Defense Evasion
T1036 – Masquerading
The infection chain masquerades as JQuery v3.7.1 and Java
T1140 – Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information
The JS on the spearphishing page deobfuscates the inauthentic CrowdStrike crash-reporting application
Table 3. Spearphishing MITRE ATT&CK mapping
Additional Resources
Read more blog posts from CrowdStrike Intelligence regarding the Falcon content issue:
Falcon Sensor Content Issue from July 19, 2024, Likely Used to Target CrowdStrike Customers
Likely eCrime Actor Uses Filenames Capitalizing on July 19, 2024, Falcon Sensor Content Issues in Operation Targeting LATAM-Based CrowdStrike Customers
Threat Actor Uses Fake CrowdStrike Recovery Manual to Deliver Unidentified Stealer
Threat Actor Distributes Python-Based Information Stealer Using a Fake Falcon Sensor Update Lure
Lumma Stealer Packed with CypherIt Distributed Using Falcon Sensor Update Phishing Lure
1 https[:]//github[.]com/jrsoftware/issrc
2 https[:]//developer.mozilla[.]org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Blob