Summary
On July 23, 2024, CrowdStrike Intelligence identified the phishing domain crowdstrike-office365[.]com, which impersonates CrowdStrike and delivers malicious ZIP and RAR files containing a Microsoft Installer (MSI) loader. The loader ultimately executes Lumma Stealer packed with CypherIt.
The domain was registered on July 23, 2024, days after July 19, 2024, when an issue present in a single content update for CrowdStrike’s Falcon sensor — which impacted Windows operating systems — was identified and a fix was deployed.
The campaign is likely linked to a June 2024 Lumma Stealer distribution campaign in which a threat actor leveraged advanced social-engineering techniques, such as using spam floods and voice phishing (vishing), to deliver malicious binaries.
Details
Phishing Domain
On July 23, 2024, the domain crowdstrike-office365[.]com served a ZIP file (SHA256 hash:
50f9c384443a40d15a6e74960f1ba75dcf741eabdb5713bd2eba453a6aad81e5
) that contains the Microsoft Installer (MSI) file WidowsSystem-update.msi (SHA256 hash:
3ed535bbcd9d4980ec8bc60cd64804e9c9617b7d88723d3b05e6ad35821c3fe7
), which is a loader.
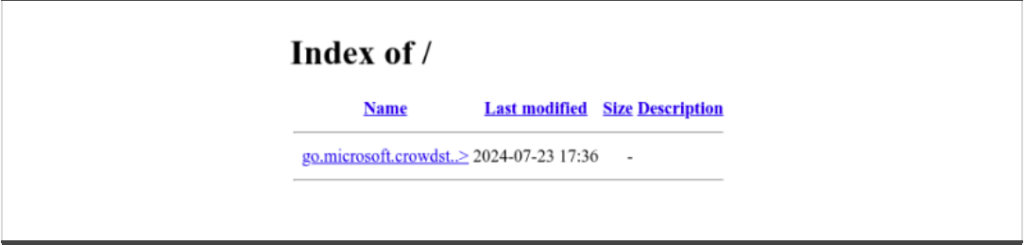
As of this writing, the domain does not appear to have a landing page and exposes an open directory containing the hosting URLs for the malicious ZIP and RAR archives (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Phishing domain content
MSI Loader
The MSI loader displays a decoy installation (Figure 2). Upon execution, the MSI extracts and executes a self-extracting RAR (SFX) file, plenrco.exe (SHA256 hash:
c3e50ca693f88678d1a6e05c870f605d18ad2ce5cfec6064b7b2fe81716d40b0
), with the command line plenrco.exe -pqwerty2023 -s1. This extracts another RAR SFX archive file stored in the PE overlay plenrco.exe. The RAR archive contains a Nullsoft Scriptable Install System (NSIS) installer with the filename SymposiumTaiwan.exe (SHA256 hash:
c1e27b2e7db4fba9f011317ff86b0d638fe720b945e933b286bb3cf6cdb60b6f
).
Figure 2. MSI file
NSIS File
The NSIS installer SymposiumTaiwan.exe contains fragments of a legitimate AutoIt executable (SHA256 hash: 865347471135bb5459ad0e647e75a14ad91424b6f13a5c05d9ecd9183a8a1cf4) and a compiled AutoIt script (SHA256 hash: 66ad1c04ebb970f2494f2f30b45d6a83c2f3a2bb663565899f57bb5422851518).
The NSIS also contains a batch script loader named Open.cmd (SHA256 hash: 6217436a326d1abcd78a838d60ab5de1fee8a62cda9f0d49116f9c36dc29d6fa), which includes useless code to hide the actual functionality. Upon execution, the Open.cmd lists processes related to security products by invoking the Windows command tasklist. If one of the processes is detected, the malware deletes itself and terminates.
The batch script then concatenates the aforementioned fragments (previously dropped to %TMP%) to two files: Dicks.pif (an AutoIt executable) and k (a compiled AutoIt script), both of which are written to the path %TMP%558563. Finally, the batch script runs the AutoIt executable, passing the compiled script as an argument.
CypherIt’s AutoIt Script
The decompiled AutoIt script (SHA256 hash: 2856b7d3948dfb5231056e52437257757839880732849c2e2a35de3103c64768) is a CypherIt loader that is heavily obfuscated to hinder static analysis. The loader implements string obfuscation (the Python re-implementation is included in Figure 3). The obfuscation is based on a subtraction with a seed, which is different for each string.
Figure 3. Python code to deobfuscate strings
Anti-Analysis
The AutoIt loader terminates if one of the following checks is met:
The hostname is tz, NfZtFbPfH or ELICZ; these hostnames are associated with antivirus (AV) emulators1
The username is test22
The file C:aaa_TouchMeNot_.txt exists; this file belongs to Windows Defender sandbox
The antivirus processes avastui.exe or bdagent.exe are running
Next-Stage Payload
The AutoIt loader contains two shellcodes for 32-bit and 64-bit systems that implement the RC4 algorithm to decrypt the final payload, which is also hardcoded within the AutoIt loader. The AutoIt script runs one of the two shellcodes depending on the system architecture.
The final payload is RC4-encrypted — with the key 656505 — and LZNT1-compressed, which results in a Lumma Stealer sample (SHA256 hash: d669078a7cdcf71fb3f2c077d43f7f9c9fdbdb9af6f4d454d23a718c6286302a; build timestamp 2024-07-19 15:01:38 UTC). The build timestamp indicates the actor highly likely built the sample for distribution the day after the single content update for CrowdStrike’s Falcon sensor was identified and a fix was deployed.
Lumma Stealer
The final payload is a Lumma Stealer executable that contacts the command-and-control (C2) server at iiaiyitre[.]pa at the time of analysis. Additional C2 URLs, listed in Table 1, were obtained from the malware’s configuration. Lumma Stealer is a commodity information stealer that collects information from browsers, including credentials, cookies, autofill data and browser-extension data.
The same C2 domain identified in this activity was observed in a recent widespread opportunistic spam flood and voice phishing (vishing) campaign in June 2024; in that campaign, the threat actor sent numerous spam emails and conducted follow-up phone calls masquerading as a “helpdesk” operator via Microsoft Teams. Based on the shared infrastructure between the campaigns and apparent targeting of corporate networks, CrowdStrike Intelligence assesses with moderate confidence that the activity is likely attributable to the same unnamed threat actor.
Recommendations
These recommendations can be implemented to help protect against the activity described in this report.
Only accept updates delivered through official CrowdStrike channels and adhere to CrowdStrike support teams’ technical guidance
Train users to avoid executing files from untrusted sources
Check website certificates on the download page to ensure downloaded software originates from a legitimate source
Use browser settings to enable download protection that can issue warnings regarding potentially harmful websites or downloads
Consider blocking AutoIt executables when not required in the corporate environment; CypherIt-packed executables use AutoIt and .pif files to run payloads
Appendix
Falcon LogScale Queries
This Falcon LogScale query detects the activity described in this alert.
// Indicators related to CSA-240849 (CSA-240849)
// hunting rule for indicators (CSA-240849)
case { in(“SHA256HashData”, values=[“1e06ef09d9e487fd54dbb70784898bff5c3ee25d87f468c9c5d0dfb8948fb45c”, “280900902df7bb855b27614884b369e5e0da25ff22efacc59443a4f593ccd145”, “3ed535bbcd9d4980ec8bc60cd64804e9c9617b7d88723d3b05e6ad35821c3fe7”, “50f9c384443a40d15a6e74960f1ba75dcf741eabdb5713bd2eba453a6aad81e5”, “66ad1c04ebb970f2494f2f30b45d6a83c2f3a2bb663565899f57bb5422851518”, “6ec39c6eee15805ef3098af7ae172517a279b042fc6c323ebf1aef8f8f2b21be”, “922b1f00115dfac831078bb5e5571640e95dbd0d6d4022186e5aa4165082c6b2”, “a992cee863a4668698af92b4f9bd427d7a827996bf09824b89beff21578b49bd”, “aca54f9f5398342566e02470854aff48c53659be0c0cb83d3ce1fd05430375f8”, “b5c0610bc01cfc3dafc9c976cb00fe7240430f0d03ec5e112a0b3f153f93b49a”, “d669078a7cdcf71fb3f2c077d43f7f9c9fdbdb9af6f4d454d23a718c6286302a”, “e6b00ee585b008f110829df68c01a62d3bfac1ffe7d65298c8a4e4109b8a7319”, “e9cd2429628e3955dd1f7c714fbaa3e3b85bfaac0bc31582cf9c5232cb8fc352”,
“bb7a19963b422ed31b0b942eeaad7388421bc270a8513337f8ec043a84a4f11c”,
“56f2aedb86d26da157b178203cec09faff26e659f6f2be916597c9dd4825d69f”]); in(“DomainName”, values=[“callosallsaospz.shop”, “crowdstrike-office365.com”, “go.microsoft.crowdstrike-office365.com”, “iiaiyitre.pa”, “indexterityszcoxp.shop”, “lariatedzugspd.shop”, “liernessfornicsa.shop”, “outpointsozp.shop”, “shepherdlyopzc.shop”, “unseaffarignsk.shop”, “upknittsoappz.shop”, “warrantelespsz.shop”]) } | table([cid, aid, #event_simpleName, ComputerName])
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Description
Detail
Hosting URL
https[:]//crowdstrike-office365[.]com/go[.]microsoft.crowdstrike-office365[.]com/download.html
Phishing Domain
crowdstrike-office365[.]com
Lumma Stealer SHA256 hash
d669078a7cdcf71fb3f2c077d43f7f9c9fdbdb9af6f4d454d23a718c6286302a
Lumma Stealer C2 URLs
iiaiyitre[.]pa
indexterityszcoxp[.]shop
lariatedzugspd[.]shop
callosallsaospz[.]shop
outpointsozp[.]shop
liernessfornicsa[.]shop
upknittsoappz[.]shop
shepherdlyopzc[.]shop
unseaffarignsk[.]shop
warrantelespsz[.]shop
iiaiyitre[.]pa
indexterityszcoxp[.]shop
lariatedzugspd[.]shop
callosallsaospz[.]shop
outpointsozp[.]shop
liernessfornicsa[.]shop
upknittsoappz[.]shop
shepherdlyopzc[.]shop
unseaffarignsk[.]shop
warrantelespsz[.]shop
Compiled AutoIt Script containing Lumma Stealer (k)
66ad1c04ebb970f2494f2f30b45d6a83c2f3a2bb663565899f57bb5422851518
NSIS installer containing AutoIt Script (SymposiumTaiwan.exe)
c1e27b2e7db4fba9f011317ff86b0d638fe720b945e933b286bb3cf6cdb60b6f
Batch script loader in NSIS installer (Open.cmd)
6217436a326d1abcd78a838d60ab5de1fee8a62cda9f0d49116f9c36dc29d6fa
Self-extracting archive containing AutoIt Script (plenrco.exe)
c3e50ca693f88678d1a6e05c870f605d18ad2ce5cfec6064b7b2fe81716d40b0
MSI files containing self-extracting archive
(UpdateMsWindows.msi,
msoffice365update.msi,
Microsoft365updater.msi,
office365crowndStrike.msi,
WidowsSystem-update.msi)
1e06ef09d9e487fd54dbb70784898bff5c3ee25d87f468c9c5d0dfb8948fb45c
e9cd2429628e3955dd1f7c714fbaa3e3b85bfaac0bc31582cf9c5232cb8fc352
bb7a19963b422ed31b0b942eeaad7388421bc270a8513337f8ec043a84a4f11c
aca54f9f5398342566e02470854aff48c53659be0c0cb83d3ce1fd05430375f8
3ed535bbcd9d4980ec8bc60cd64804e9c9617b7d88723d3b05e6ad35821c3fe7
RAR and ZIP files containing MSI files
(UpdateMSwindows.rar,
UpdateMSwindows.rar,
msoffice365update.rar,
msoffice365update.zip,
office365crowndStrike.rar,
office365crowndStrike.zip,
WidowsSystem-update.zip)
6ec39c6eee15805ef3098af7ae172517a279b042fc6c323ebf1aef8f8f2b21be
922b1f00115dfac831078bb5e5571640e95dbd0d6d4022186e5aa4165082c6b2
56f2aedb86d26da157b178203cec09faff26e659f6f2be916597c9dd4825d69f
e6b00ee585b008f110829df68c01a62d3bfac1ffe7d65298c8a4e4109b8a7319
b5c0610bc01cfc3dafc9c976cb00fe7240430f0d03ec5e112a0b3f153f93b49a
280900902df7bb855b27614884b369e5e0da25ff22efacc59443a4f593ccd145
a992cee863a4668698af92b4f9bd427d7a827996bf09824b89beff21578b49bd
Table 1. Indicators of compromise
MITRE ATT&CK
This table details the MITRE ATT&CK® tactics and techniques described in this report.
Tactic
Technique
Observable
Initial Access
T1566 – Phishing
The malicious MSI is distributed via a phishing domain
Execution
T1059.003 – Command and Scripting Interpreter: Windows Command Shell
The NSIS installer contains a batch script that deletes the malware if security products are detected
T1204 – User Execution
The user is prompted to install the malicious executable, which masquerades as an MSI file
Defense Evasion
T1027.002 – Obfuscated Files or Information: Software Packing
Lumma Stealer is packed using CipherIT
Exfiltration
T1041 – Exfiltration Over C2 Channel
Lumma Stealer sends all exfiltrated data to its C2 server
Table 2. MITRE ATT&CK mapping
1 https[:]//www[.]usenix[.]org/system/files/conference/woot16/woot16-paper-blackthorne_update[.]pdf
Additional Resources
Read other blog posts from CrowdStrike Intelligence regarding the Falcon content issue:
Falcon Sensor Content Issue from July 19, 2024, Likely Used to Target CrowdStrike Customers
Likely eCrime Actor Uses Filenames Capitalizing on July 19, 2024, Falcon Sensor Content Issues in Operation Targeting LATAM-Based CrowdStrike Customers
Threat Actor Uses Fake CrowdStrike Recovery Manual to Deliver Unidentified Stealer
Threat Actor Distributes Python-Based Information Stealer Using a Fake Falcon Sensor Update Lure